Animation Overview
Animation is a method in which pictures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film.
There are 5 mediums or types of animation
● Cel (Celluloid) Animation This is the original hand-drawn cel animation, where the artist literally has to draw thousands of images on special paper and have them photographed, frame by frame.
● 2D Animation – Done on a computer with the help from software like Flash, AE, etc.
● 3D Animation – Software like Maya, Max, etc
● Motion Graphics – Done with help from After Effects, etc
● Stop Motion – Stop motion is like traditional animation, except instead of drawing, you have clay models and a set that you have to carefully manipulate to produce animation
Today, most animations are 3D Animations made with computer-generated imagery (CGI).
For an overview of the pipeline for animation, we’ll take the example of 3D animation, or CGI.
So when a student says they want to learn animation, it is a vague request because what they are really asking is that they want to learn a medium, not knowing that the medium has more features.
The right question students should ask is which part of the specific feature of the animation medium they should learn.
Since we now know that the term animated movie is a generalised term for a CGI movie, let’s go deeper and see what categories there are in this CGI medium.
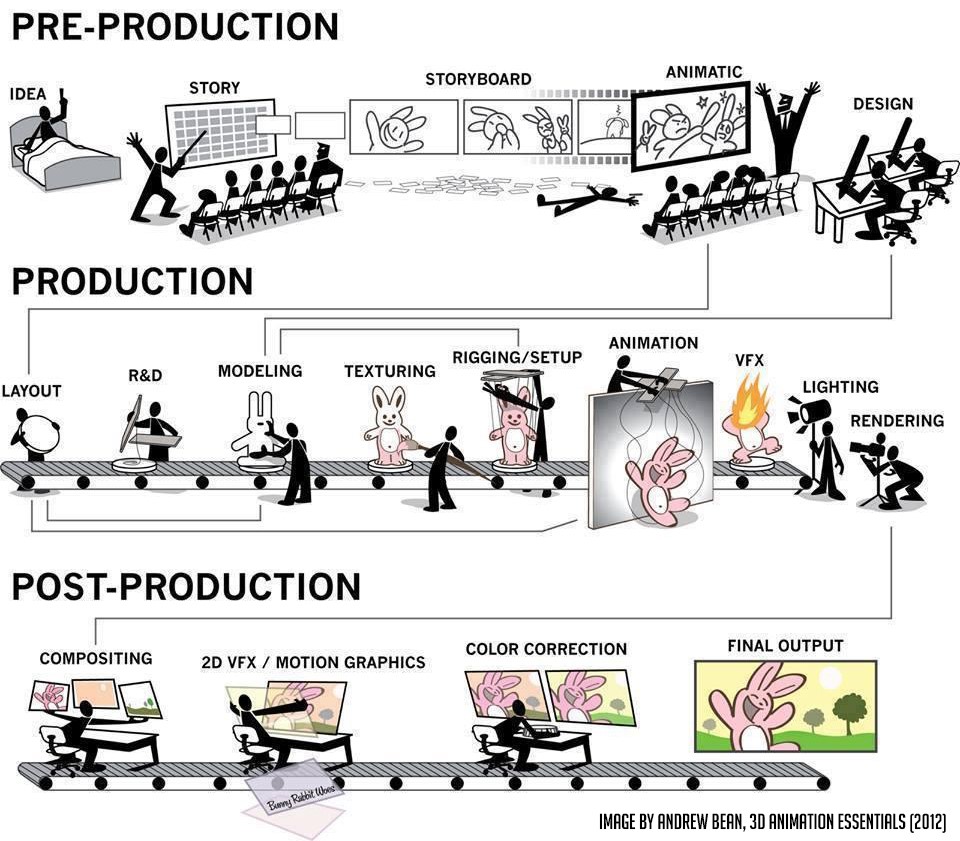
MOVIE MAKING PROCESS (CGI)
Any movie follows a process, it starts with an idea, goes through multiple departments, and ultimately ends up in a theater. This process is broadly classified into three stages preproduction, production, and PostProduction.
Making a movie is a complicated affair. You can’t play with other people’s time or money, and there’s always tremendous pressure to deliver every single day. The point of the above simplistic comparison is to show that cooking does not begin when you put your ingredients in the oven. Cooking begins a whole lot earlier.
Preproduction is the stage where you prepare for cooking. This stage is further divided into subcategories. They are, namely-
Script: It is a story idea for the movie written down by the screenwriter. It’s basically the structure of the whole movie, with complete plots, characters, and tone.
StoryBoard : The script becomes the foundation for the storyboard. A storyboard is a graphic representation of how your video will unfold, shot by shot. Like a script, your storyboard visually guides you throughout the production process. By planning your video, you know which shots you need to create and how to create them when filming begins. You can get others’ feedback early on and make simple adjustments to your storyboard, rather than making major changes while filming.
Character Design : It is one of the most important stages of pre-production. This is where we sketch out our characters for the movie.
Usually you’ll be provided with a physical or psychological description of the character, but it’s not necessary yet to stick 100% to them in all your sketches, since the important thing is to explore the widest range of possibilities for a character and hopefully have a lot of contrast between them. How does this character look? Tall/short, fat/thin, muscular/weak, white/black, Asian or Latino? Even in some cases, you could try drawing the opposite of the gender that was assigned.
Dialogue Recording : The script is needed for dialogue and extra sound effects. The actors will read the lines from the script and record their dialogue. These voices will be used later on for the animatic and for the final animation.
In some big budget animated movies, the studio hires some big Hollywood stars to give the voiceovers for the characters in the movie.
Animatic: Simply put, an animatic is an animated storyboard. It is a series of images played in sequence. StoryBoards are brought into an editing program and are cut together with the correct timing and pace of the film. They include basic sound effects, dialogue recordings, and scratch soundtracks.
Production : is the stage where you actually do the Cooking. This is the stage where students get confused with the general term animation’. This is further subdivided into more subcategories, and with these categories, students can choose in which department they want to specialise in.
3D Modelling : It is a technique in computer graphics for producing a 3D digital representation of any character or object. So once the design of the character or object is ready, we sculpt this character design into a 3D environment using softwares like Maya, etc. An artist uses these programs to manipulate points in virtual space (called vertices) to form a mesh: a collection of vertices that form an object. It is like taking a piece of clay and modifying it by applying pressure to some parts and pulling on some parts until a desired shape is achieved. Only the same process is done in a 3D environment.
Surfacing/Texturing : Once the 3D model is ready, it needs to be coloured as it is in grayscale. Surfacing artists are master digital painters. They enhance the appearance of modelled characters, props, and environments in an animated feature film according to the visual style set forth by the art director and director of the film.
Rigging: Rigging is essentially putting bones into your mesh (the 3D model). When you make a rig, you add joints, all of which are connected by (the accurately named) bones. When you’re done creating the rig, it should have a very similar structure to the bones of the human’s/creature’s skeletal structure. This can also be done for inanimate objects to give control over certain moving parts, like car tires. The rig allows you to manipulate limbs and – depending on the complexity of the rig – smaller details like facial expression, thereby granting you the ability to move the mesh without having to animate every individual vertex.
3D Animation : Once the Modelling, Rigging and Texturing is done of a character are done, it is ready to be animated. With the help of the software, we can move the rigged model. Careful manipulation of 3D models or objects is carried out within 3D software for creating snapshots of sequences, giving them the illusion of animation or movement. However, this is completely based on the technique used for manipulating the objects, and this is how one can make the character walk, run, cry, or laugh.
PostProduction : Post-production is the final stage in the process of creating an animated movie, where everything comes together. It is also divided into few departments.
Lighting: Simply put, it is a process where we put the light in the shot to indicate what time of day or night it is currently in the scene. Although it is far more complex than that. It often happens that a well-modeled 3D object looks unconvincing, flat, or even plastic because of a badly implemented lighting solution. On the other hand, well-chosen lighting techniques can significantly enhance the project’s value.
Visual Fx : Also called special effects, this is where we create explosions, fire, water and smoke effects, There are several other things we can do like crowd simulation, particle dynamics, etc.
Final Editing / Compositing : It involves exporting or rendering out the animation frames and then editing the pieces of animation together using video editing software. The sound track, including sound effects, is also added during the final edit.
So these are mostly major departments through which any movie goes; no one department is wholly responsible for the movie; it’s a combined effort. Everyone plays a significant role in this process.
Hopefully I was able to show the workings of each department, which will be helpful for the student as to which line suits them well.
Similar Articles
-
AI is Revolutionizing the Gaming Industry 10-14-2025
Ever been outsmarted by a clever enemy in a video game, or wondered how a…
-

ACES COLOR SPACE IN VISUAL EFFECTS 10-10-2025
ACES, which stands for the Academy Color Encoding System, is a standardized color management system…
-

The Future of 3D Game Art (2025): Trends, Tools & New Roles Every Studio Needs 09-23-2025
Game art is no longer just “model, texture, animate.” With real-time engines (UE5/modern Unity), procedural…
-

Ignite Your Ink: Why You Should Be Part of Inktober 2025 09-17-2025
Hey budding artists ? Every year, artists around the world challenge themselves to draw one…