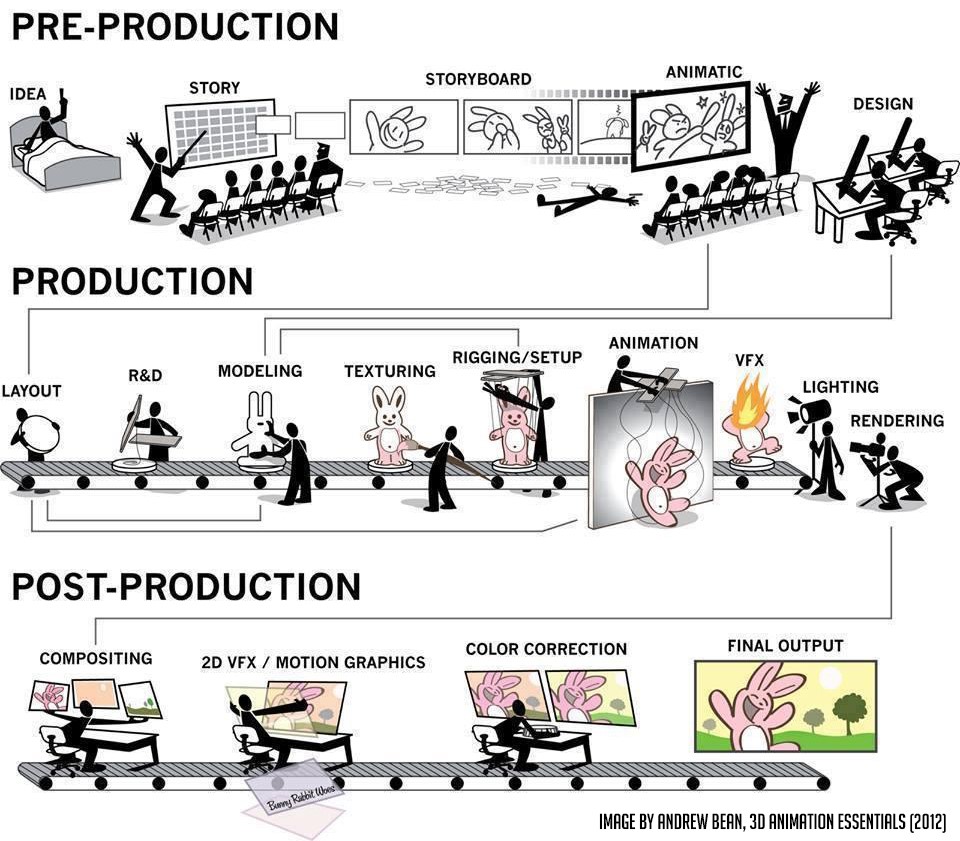
Mastering 2D and 3D Animation

The Ultimate Career Boost in Today’s Creative Industry
The demand for skilled animators is skyrocketing in today’s fast-paced digital world. From blockbuster movies and video games to advertising and virtual reality, animation has become integral to countless industries. But what sets apart the average animator from the truly exceptional? The answer lies in mastering advanced 2D and 3D animation skills. These abilities are not just tools—they are game-changers that can propel your career to new heights. Here’s why.
The Power of Advanced Animation Skills
Animation is no longer just about creating moving images; it’s about storytelling, innovation, and pushing creative boundaries. Advanced 2D and 3D animation skills allow you to bring ideas to life in ways that captivate audiences and solve complex visual challenges. Whether you’re crafting a heartwarming character for a children’s show or designing a hyper-realistic environment for a video game, these skills enable you to stand out in a competitive field.
Why 2D Animation Still Matters
While 3D animation often steals the spotlight, 2D animation remains a powerful and versatile medium. It’s the foundation of animation, and mastering it can enhance your understanding of movement, timing, and composition. Advanced 2D skills are particularly valuable in industries like advertising, where simplicity and clarity are key, or in indie game development, where a unique art style can make a project unforgettable. Plus, with the rise of platforms like YouTube and social media, 2D animation is more accessible and in demand than ever.
The Rise of 3D Animation
3D animation, on the other hand, has revolutionized the entertainment and tech industries. From Pixar’s iconic films to the immersive worlds of virtual reality, 3D animation is at the forefront of innovation. Advanced 3D skills, such as rigging, lighting, and texturing, allow you to create lifelike characters and environments that resonate with audiences. Moreover, industries like architecture, healthcare, and education are increasingly relying on 3D animation for simulations, presentations, and training programs, opening up even more career opportunities.
A Competitive Edge in the Job Market
The animation industry is highly competitive, and employers are constantly seeking professionals who can deliver exceptional results. By honing advanced 2D and 3D animation skills, you position yourself as a versatile and valuable asset. Studios and companies are more likely to hire animators who can handle multiple aspects of a project, from concept art to final rendering. Additionally, these skills often come with higher earning potential, as specialized expertise is always in demand.
Adapting to Industry Trends
The animation industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies like AI, motion capture, and real-time rendering reshaping the landscape. Advanced animators who stay ahead of these trends are better equipped to adapt and thrive. For instance, learning how to integrate AI tools into your workflow can streamline processes and enhance creativity. Similarly, mastering real-time rendering techniques can make you indispensable in the gaming and VR sectors.
Building a Diverse Portfolio
One of the best ways to showcase your talent is through a diverse portfolio. Advanced 2D and 3D animation skills allow you to create a wide range of projects, from short films and commercials to interactive experiences and architectural visualizations. A strong portfolio not only demonstrates your technical abilities but also your creativity and problem-solving skills, making you a standout candidate for any role.
How to Get Started
If you’re ready to take your animation career to the next level, investing in advanced training is essential. Enroll in specialized courses, attend workshops, and practice consistently to refine your skills. Networking with industry professionals and staying updated on the latest tools and trends can also give you a competitive edge. Remember, the journey to mastery is ongoing, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
Conclusion
Advanced 2D and 3D animation skills are more than just technical abilities—they are transformative tools that can unlock endless opportunities in your career. Whether you’re aiming to work in film, gaming, advertising, or beyond, these skills will set you apart and help you achieve your professional goals. So, take the leap, embrace the challenge, and watch as your career soars to new heights. The future of animation is bright, and with the right skills, you can be at the forefront of it all.
Similar Articles
-

Mastering 2D and 3D Animation 03-04-2025
The Ultimate Career Boost in Today’s Creative Industry The demand fo
-

The Changing Face of the Animation Industry 02-27-2025
The animation industry has undergone a seismic transformation over the
-

Why the Design Industry is the Future? 02-25-2025
A Guide for Creative Students After 12th The 12th grade is a turning p
-

The Digital Canvas: Explore Creative Careers Now 02-24-2025
The creative industry is undergoing a massive transformation, driven b